Security
The Hitchhiker's Guide to Observability - Adding A New Tenant - Part 6
While we have created our distributed tracing infrastructure, we created two tenants as an example. In this article, I will show you how to add a new tenant and which changes must be made in the TempoStack and the OpenTelemetry Collector.
This article was mainly created as a quick reference guide to see which changes must be made when adding new tenants.
The Hitchhiker's Guide to Observability - Understanding Traces - Part 5
With the architecture established, TempoStack deployed, the Central Collector configured, and applications generating traces, it’s time to take a step back and understand what we’re actually building. Before you deploy more applications and start troubleshooting performance issues, you need to understand how to read and interpret distributed traces.
Let’s decode the matrix of distributed tracing!
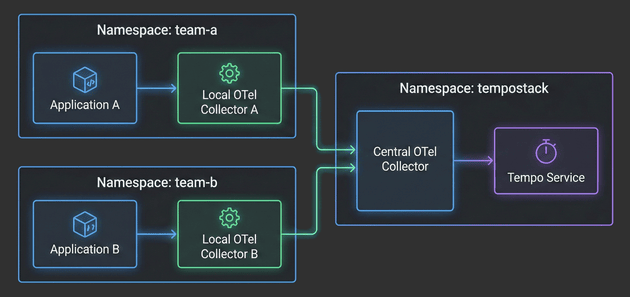
The Hitchhiker's Guide to Observability - Example Applications - Part 4
With the architecture defined, TempoStack deployed, and the Central Collector configured, we’re now ready to complete the distributed tracing pipeline. It’s time to deploy real applications and see traces flowing through the entire system!
In this fourth installment, we’ll focus on the application layer - deploying Local OpenTelemetry Collectors in team namespaces and configuring example applications to generate traces. You’ll see how applications automatically get enriched with Kubernetes metadata, how namespace-based routing directs traces to the correct TempoStack tenants, and how the entire two-tier architecture comes together.
The Hitchhiker's Guide to Observability - Central Collector - Part 3
With the architecture defined in Part 1 and TempoStack deployed in Part 2, it’s time to tackle the heart of our distributed tracing system: the Central OpenTelemetry Collector. This is the critical component that sits between your application namespaces and TempoStack, orchestrating trace flow, metadata enrichment, and tenant routing.
The Hitchhiker's Guide to Observability - Grafana Tempo - Part 2
After covering the fundamentals and architecture in Part 1, it’s time to get our hands dirty! This article walks through the complete implementation of a distributed tracing infrastructure on OpenShift.
We’ll deploy and configure the Tempo Operator and a multi-tenant TempoStack instance. For S3 storage we will use the integrated OpenShift Data Foundation. However, you can use whatever S3-compatible storage you have available.
The Hitchhiker's Guide to Observability Introduction - Part 1
With this article I would like to summarize and, especially, remember my setup. This is Part 1 of a series of articles that I split up so it is easier to read and understand and not too long. Initially, there will be 6 parts, but I will add more as needed.
What's new in OpenShift, 4.20 Edition
This article covers news and updates in the OpenShift 4.20 release. We focus on points that got our attention, but this is not a complete summary of the release notes.
Red Hat Quay Registry - Integrate Keycloak
This guide shows you how to configure Keycloak as an OpenID Connect (OIDC) provider for Red Hat Quay Registry. It covers what to configure in Keycloak, what to put into Quay’s config.yaml (or Operator config), how to verify the login flow, and how to switch your Quay initial/admin account (stored locally in Quay’s DB) to an admin user that authenticates via Keycloak.
A second look into the Kubernetes Gateway API on OpenShift
This is our second look into the Kubernetes Gateway API an it’s integration into OpenShift. This post covers TLS configuration.
The Kubernetes Gateway API is new implementation of the ingress, load balancing and service mesh API’s. See upstream for more information.
Also the OpenShift documentation provides an overview of the Gateway API and it’s integration.
We demonstrate how to add TLS to our Nginx deployment, how to implement a shared Gateway and finally how to implement HTTP to HTTPS redirection with the Gateway API. Furthermore we cover how HTTPRoute objects attach to Gateways and dive into ordering of HTTPRoute objects.
A first look into the Kubernetes Gateway API on OpenShift
This blog post summarizes our first look into the Kubernetes Gateway API and how it is integrated in OpenShift.
[Ep.14] Reusable Argo CD Application Template
When working with Argo CD at scale, you often find yourself creating similar Application manifests repeatedly. Each application needs the same basic structure but with different configurations for source repositories, destinations, and sync policies. Additionally, managing namespace metadata becomes tricky when you need to conditionally control whether Argo CD should manage namespace metadata based on sync options.
In this article, I’ll walk you through a reusable Helm template that solves these challenges by providing a flexible, DRY (Don’t Repeat Yourself) approach to creating Argo CD Applications. This template is available in my public Helm Chart library and can easily be used by anyone.
Cert-Manager Policy Approver in OpenShift
One of the most commonly deployed operators in OpenShift environments is the Cert-Manager Operator. It automates the management of TLS certificates for applications running within the cluster, including their issuance and renewal.
The tool supports a variety of certificate issuers by default, including ACME, Vault, and self-signed certificates. Whenever a certificate is needed, Cert-Manager will automatically create a CertificateRequest resource that contains the details of the certificate. This resource is then processed by the appropriate issuer to generate the actual TLS certificate. The approval process in this case is usually fully automated, meaning that the certificate is issued without any manual intervention.
But what if you want to have more control? What if certificate issuance must follow strict organizational policies, such as requiring a specifc country code or organization name? This is where the CertificateRequestPolicy resource, a resource provided by the Approver Policy, comes into play.
This article walks through configuring the Cert-Manager Approver Policy in OpenShift to enforce granular policies on certificate requests.
Single log out from Keycloak and OpenShift
The following 1-minute article is a follow-up to my previous article about how to use Keycloak as an authentication provider for OpenShift. In this article, I will show you how to configure Keycloak and OpenShift for Single Log Out (SLO). This means that when you log out from Keycloak, you will also be logged out from OpenShift automatically. This requires some additional configuration in Keycloak and OpenShift, but it is not too complicated.
Step by Step - Using Keycloak Authentication in OpenShift
I was recently asked about how to use Keycloak as an authentication provider for OpenShift. How to install Keycloak using the Operator and how to configure Keycloak and OpenShift so that users can log in to OpenShift using OpenID. I have to admit that the exact steps are not easy to find, so I decided to write a blog post about it, describing each step in detail. This time I will not use GitOps, but the OpenShift and Keycloak Web Console to show the steps, because before we put it into GitOps, we need to understand what is actually happening.
This article tries to explain every step required so that a user can authenticate to OpenShift using Keycloak as an Identity Provider (IDP) and that Groups from Keycloak are imported into OpenShift. This article does not cover a production grade installation of Keycloak, but only a test installation, so you can see how it works. For production, you might want to consider a proper database (maybe external, but at least with a backup), high availability, etc.).
Copyright © 2020 - 2026 Toni Schmidbauer & Thomas Jungbauer