Using ServerSideApply with ArgoCD
- - 3 min read
„If it is not in GitOps, it does not exist“ - However, managing objects partially only by Gitops was always an issue, since ArgoCD would like to manage the whole object. For example, when you tried to work with node labels and would like to manage them via Gitops, you would need to put the whole node object into ArgoCD. This is impractical since the node object is very complex and typically managed by the cluster. There were 3rd party solutions (like the patch operator), that helped with this issue.
However, with the Kubernetes feature Server-Side Apply this problem is solved. Read further to see a working example of this feature.
What is Server-Side Apply (SSA)
Quoting from Kuberneted Documentation:
Server-Side Apply helps users and controllers manage their resources through declarative configurations. Clients can create and modify their objects declaratively by sending their fully specified intent.
A fully specified intent is a partial object that only includes the fields and values for which the user has an opinion. That intent either creates a new object or is combined, by the server, with the existing object.
In other words: you can send a snippet of an object to the cluster and the cluster will eventually combine everything on the server and not validate on the client side first. All you need is a way to identify the object. Usually, the name and maybe the namespace too.
SSA and ArgoCD
When it comes to GitOps the implementation of SSA is quite new. However, it is important to note, that (managed field) conflicts are currently not handled by ArgoCD. Instead, ArgoCD forces a change and overrides everything, even if the field is managed by somebody else. This might be improved in the future. Nevertheless … let’s test the feature.
Prerequisites
The support of the Server-Side Apply feature is currently available in the latest version of ArgoCD. This means, that the channel of the openshift-gitops operator must be changed to "latest", which will deploy openshift-gitops version 1.6
A new stable version will arrive soon. :)
Node Labelling Chart
In this example, I would like to use a Helm chart that will try to set two different labels on 2 nodes. This is a very easy example to demonstrate the feature.
As a Helm chart, I have prepared the following: https://github.com/tjungbauer/openshift-clusterconfig-gitops/tree/main/clusters/management-cluster/node-configuration
The values for this chart are straightforward: per node, a list of custom labels is defined.
helper-server-side-apply:
nodes: (1)
- name: ip-10-0-233-237.us-west-1.compute.internal (2)
enabled: true
custom_labels: (3)
environment: 'Production'
gpu: false
- name: ip-10-0-193-67.us-west-1.compute.internal
enabled: true
custom_labels:
environment: 'Test'
gpu: true| 1 | List of nodes |
| 2 | Node name as OpenShift knows the node (oc get nodes) |
| 3 | List of labels that should be added to the node: here environment and gpu |
| The Chart is using a sub-chart called helper-server-side-apply. The source can be found at the Helm Repository |
The output of this Helm Chart will be the following:
# Source: node-labels/charts/helper-server-side-apply/templates/node.yaml
kind: Node
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: "ip-10-0-233-237.us-west-1.compute.internal" (1)
labels:
gitops.ownedBy: openshift-gitops
helm.sh/chart: helper-server-side-apply-1.0.3
app.kubernetes.io/name: helper-server-side-apply
app.kubernetes.io/instance: release-name
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
environment: "Production" (2)
gpu: "false" (3)
---
# Source: node-labels/charts/helper-server-side-apply/templates/node.yaml
kind: Node
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: "ip-10-0-193-67.us-west-1.compute.internal"
labels:
gitops.ownedBy: openshift-gitops
helm.sh/chart: helper-server-side-apply-1.0.3
app.kubernetes.io/name: helper-server-side-apply
app.kubernetes.io/instance: release-name
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
environment: "Test"
gpu: "true"| 1 | The name of the node and our identifier |
| 2 | The first label we set |
| 3 | The second label we set |
| This is not a full definition of a Node object. The only things defined are the node name and the labels. (Besides the customer labels we would like to add, some default labels are added automatically.) |
ArgoCD Application
So we have a Helm chart in Git. Perfect, but to automate everything with Gitops we need to create the object Application. For example the following:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: node-labelling
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
destination:
namespace: default
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
info:
- name: Description
value: Deploy Node Labels
project: default
source:
helm:
valueFiles:
- values.yaml
path: clusters/management-cluster/node-configuration (1)
repoURL: 'https://github.com/tjungbauer/openshift-clusterconfig-gitops'
targetRevision: main
syncPolicy:
syncOptions:
- ServerSideApply=true (2)
- Validate=false (3)| 1 | Path and URL of the node labelling Helm chart |
| 2 | Must be set to true to enable SSA |
| 3 | Must be set to false to skip schema validation |
| The two syncOptions are important to set. Since the yaml output might not pass the validation, the schema validation should be disabled. |
This will create the following application in ArgoCD:
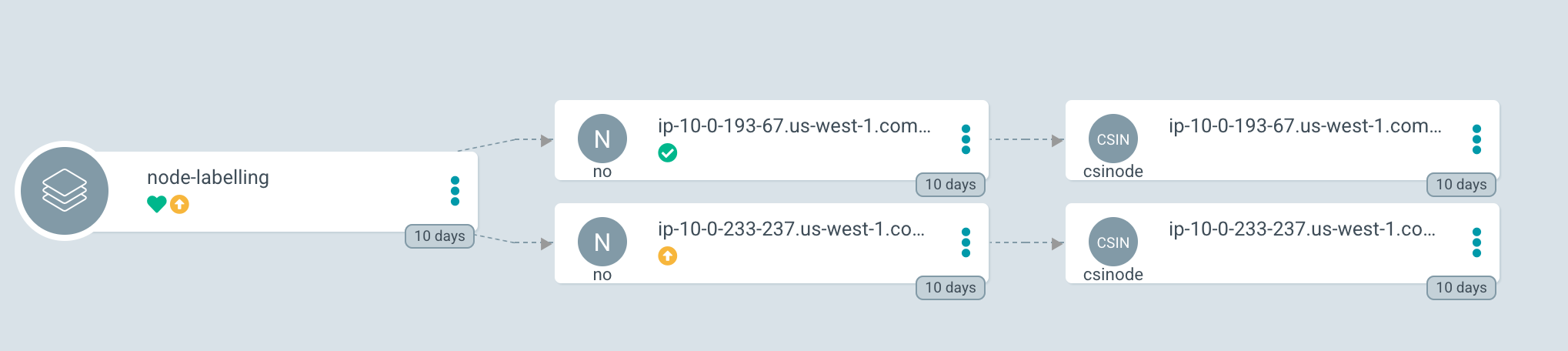
Syncing the Application
When you now synchronize the ArgoCD application, ArgoCD will take the yaml and will tell Kubernetes (or OpenShift) to perform a Server-Side Apply. This will result in the following yaml for the node:
kind: Node
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: ip-10-0-193-67.us-west-1.compute.internal
labels:
beta.kubernetes.io/os: linux
app.kubernetes.io/instance: node-labelling
[...]
node-role.kubernetes.io/worker: ''
gitops.ownedBy: openshift-gitops
[...]
environment: Test
[...]That’s it … all the magic is done.
Copyright © 2020 - 2025 Toni Schmidbauer & Thomas Jungbauer
 Thomas Jungbauer
Thomas Jungbauer